« Conditional Display » : différence entre les versions
Aller à la navigation
Aller à la recherche
Aucun résumé des modifications |
Aucun résumé des modifications |
||
| Ligne 1 : | Ligne 1 : | ||
Conditional display is simply managed with « <font color=#FF8C00>if</font> » or « <font color=#FF8C00>switch</font> » and using the <font color=#4169E1>generic()</font> method (or the <font color=#4169E1>display()</font> method for specific treatments): | Conditional display is simply managed with « <font color=#FF8C00>if</font> » or « <font color=#FF8C00>switch</font> » and using the <font color=#4169E1>generic()</font> method (or the <font color=#4169E1>display()</font> method for specific treatments): | ||
<pre class="brush: | <pre class="brush:Java"> | ||
public class myPanel extends GPanel { | public class myPanel extends GPanel { | ||
Version du 2 mai 2017 à 14:15
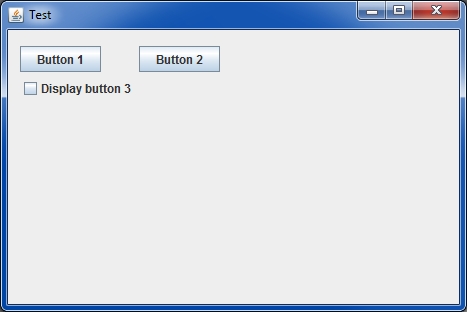
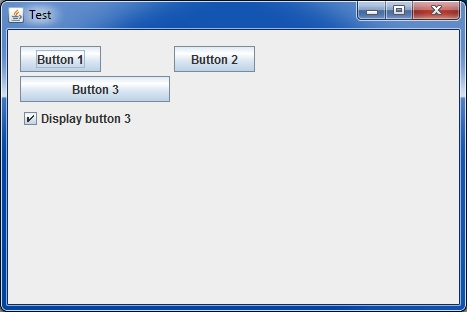
Conditional display is simply managed with « if » or « switch » and using the generic() method (or the display() method for specific treatments):
public class myPanel extends GPanel {
GButton but1;
GButton but2;
GButton but3;
GCheckBox cb;
public myPanel() {
but1 = new GButton("Bouton 1");
but2 = new GButton("Bouton 2");
but3 = new GButton("Bouton 3");
cb = new GCheckBox("Display button 3");
}
public void generic() throws GException {
put(but1);
put(but2);
if ( cb.isSelected() ) { put(but3); } // Easy, isn't it ?
put(cb);
}