« Units management » : différence entre les versions
Page créée avec « TBW ... Return to the introduction ↑ Go to the next page → » |
Aucun résumé des modifications |
||
| Ligne 1 : | Ligne 1 : | ||
Units are managed with the [{{PathCurrentJavaDoc}}/fr/cnes/genius/unit/GUnit.html|GUnit]] class or more directly with [{{PathCurrentJavaDoc}}/fr/cnes/genius/unit/GMetricUnit.html|GMetricUnit]]. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
// To display a menu allowing to display kilometers (km) or Nautic Miles (nmi) | |||
GUnit[] unitDis = { new GMetricUnit ("km") , new GMetricUnit ("nmi") }; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
In case of using [{{PathCurrentJavaDoc}}/fr/cnes/genius/unit/GMetricUnit.html|GMetricUnit]], when we define a unit for a real value, it is stored automatically in the computer memory in '''International System (IS)''' (m, kg, rad …). | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
dist = new GEntryReal("Distance", 1000., unitDis); // Initialization with 1000 meters. | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
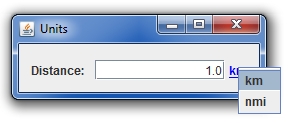
Thus, in that case, we may have a difference between what it is displayed (for example 1.0 km) and what it is actually stored in the memory (1000.). | |||
[[File:Units.jpg]] | |||
To get the value stored in memory (same for an integer even if there is no units for it), we will use the <font color=#4169E1>getValue()</font> method: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
double val = dist.getValue(); // Allways in IS | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
The basic '''IS''' units given by default by <font color=#556B2F>**GENIUS**</font> are the following: | |||
* kilogram (**kg**) | |||
* meter (**m**) | |||
* second (**s**) | |||
* Amper (**A**) | |||
Of course, <font color=#556B2F>**GENIUS**</font> proposes also angular units with **radian** (rad) for IS to be convertible in **degree** (deg). | |||
Then, it is possible to get composed units using "**.**" for multiplication, "**/**" for division or "**^**" for power (a negative power is enabled). Thus, we may have **kg.m/s^2** (or **kg.m.s^-2**) as a composed unit. | |||
Allways about composed units, <font color=#556B2F>**GENIUS**</font> proposes the following ones: | |||
* Steradians (m<sup>2</sup>.m<sup>-2</sup>) => **sr** | |||
* Hertz (s<sup>-1</sup>) => **Hz** | |||
* Newton (kg.m.s<sup>-2</sup>) => **N** | |||
* Pascal (N.m<sup>-2</sup>) => **Pa** | |||
* Joules (N.m) => **J** | |||
* Watt (J.s<sup>-1</sup>) => **W** | |||
* Coulomb (A.s) => **C** | |||
* Volt (W.A<sup>-1</sup>) => **V** | |||
* Farad (C.V<sup>-1</sup>) => **F** | |||
* Ohm (V.A<sup>-1</sup>) => **R** | |||
For more facilities, these units have also been added: | |||
* gramm = 0.001*kg => **g** | |||
* ton = 1000 kg => **t** | |||
* minutes = 60 s => **mn** | |||
* hour = 3600 s => **h** | |||
* day = 86400 => **j** | |||
It is also possible to use coefficients: | |||
* **T** : Tera = 10<sup>12</sup> | |||
* **G** : Giga = 10<sup>9</sup> | |||
* **M** : Mega = 10<sup>6</sup> | |||
* **k** : kilo = 10<sup>3</sup> | |||
* **h** : hecto = 10<sup>2</sup> | |||
* **da** : deca = 10 | |||
* **d** : deci = 10<sup>-1</sup> | |||
* **c** : centi = 10<sup>-2</sup> | |||
* **m** : mili = 10<sup>-3</sup> | |||
* **u** : micro = 10<sup>-6</sup> | |||
* **n** : nano = 10<sup>-9</sup> | |||
* **p** : pico = 10<sup>-12</sup> | |||
Note that for mass values, these coefficient will be applied on "'''g'''" and not "'''kg'''". | |||
So, we could have something as '''mg.dam/mn^2''' ... for something equivalent as (1/36)10-6 Newtons ! | |||
At last, for not proportional conversions, <font color=#556B2F>**GENIUS**</font> proposes anyway to convert: | |||
* Kelvin (**K**) to Celsius (**C**) or Fahrenheit (**F**) (using [{{PathCurrentJavaDoc}}/fr/cnes/genius/unit/GTemperatureUnit.html|GTemperatureUnit]]) | |||
* "**%**" to "**‰**" (using [{{PathCurrentJavaDoc}}/fr/cnes/genius/unit/GPercentUnit.html|GPercentUnit]]). | |||
[[WELCOME_TO_THE_GENIUS_WIKI|Return to the introduction ↑]] | [[WELCOME_TO_THE_GENIUS_WIKI|Return to the introduction ↑]] | ||
[[GContainer|Go to the next page →]] | [[GContainer|Go to the next page →]] | ||
Version du 5 mai 2017 à 09:08
Units are managed with the [1]] class or more directly with [2]].
// To display a menu allowing to display kilometers (km) or Nautic Miles (nmi)
GUnit[] unitDis = { new GMetricUnit ("km") , new GMetricUnit ("nmi") };
In case of using [3]], when we define a unit for a real value, it is stored automatically in the computer memory in International System (IS) (m, kg, rad …).
dist = new GEntryReal("Distance", 1000., unitDis); // Initialization with 1000 meters.
Thus, in that case, we may have a difference between what it is displayed (for example 1.0 km) and what it is actually stored in the memory (1000.).
To get the value stored in memory (same for an integer even if there is no units for it), we will use the getValue() method:
double val = dist.getValue(); // Allways in IS
The basic IS units given by default by **GENIUS** are the following:
- kilogram (**kg**)
- meter (**m**)
- second (**s**)
- Amper (**A**)
Of course, **GENIUS** proposes also angular units with **radian** (rad) for IS to be convertible in **degree** (deg).
Then, it is possible to get composed units using "**.**" for multiplication, "**/**" for division or "**^**" for power (a negative power is enabled). Thus, we may have **kg.m/s^2** (or **kg.m.s^-2**) as a composed unit.
Allways about composed units, **GENIUS** proposes the following ones:
- Steradians (m2.m-2) => **sr**
- Hertz (s-1) => **Hz**
- Newton (kg.m.s-2) => **N**
- Pascal (N.m-2) => **Pa**
- Joules (N.m) => **J**
- Watt (J.s-1) => **W**
- Coulomb (A.s) => **C**
- Volt (W.A-1) => **V**
- Farad (C.V-1) => **F**
- Ohm (V.A-1) => **R**
For more facilities, these units have also been added:
- gramm = 0.001*kg => **g**
- ton = 1000 kg => **t**
- minutes = 60 s => **mn**
- hour = 3600 s => **h**
- day = 86400 => **j**
It is also possible to use coefficients:
- **T** : Tera = 1012
- **G** : Giga = 109
- **M** : Mega = 106
- **k** : kilo = 103
- **h** : hecto = 102
- **da** : deca = 10
- **d** : deci = 10-1
- **c** : centi = 10-2
- **m** : mili = 10-3
- **u** : micro = 10-6
- **n** : nano = 10-9
- **p** : pico = 10-12
Note that for mass values, these coefficient will be applied on "g" and not "kg".
So, we could have something as mg.dam/mn^2 ... for something equivalent as (1/36)10-6 Newtons !
At last, for not proportional conversions, **GENIUS** proposes anyway to convert: